
Adrenaline chemical formula Royalty Free Vector Image
Background: Adrenaline is localized to specific regions of the central nervous system (CNS), but its role therein is unclear because of a lack of suitable pharmacologic agents. Ideally, a chemical is required that crosses the blood-brain barrier, potently inhibits the adrenaline-synthesizing enzyme PNMT, and does not affect other catecholamine processes.
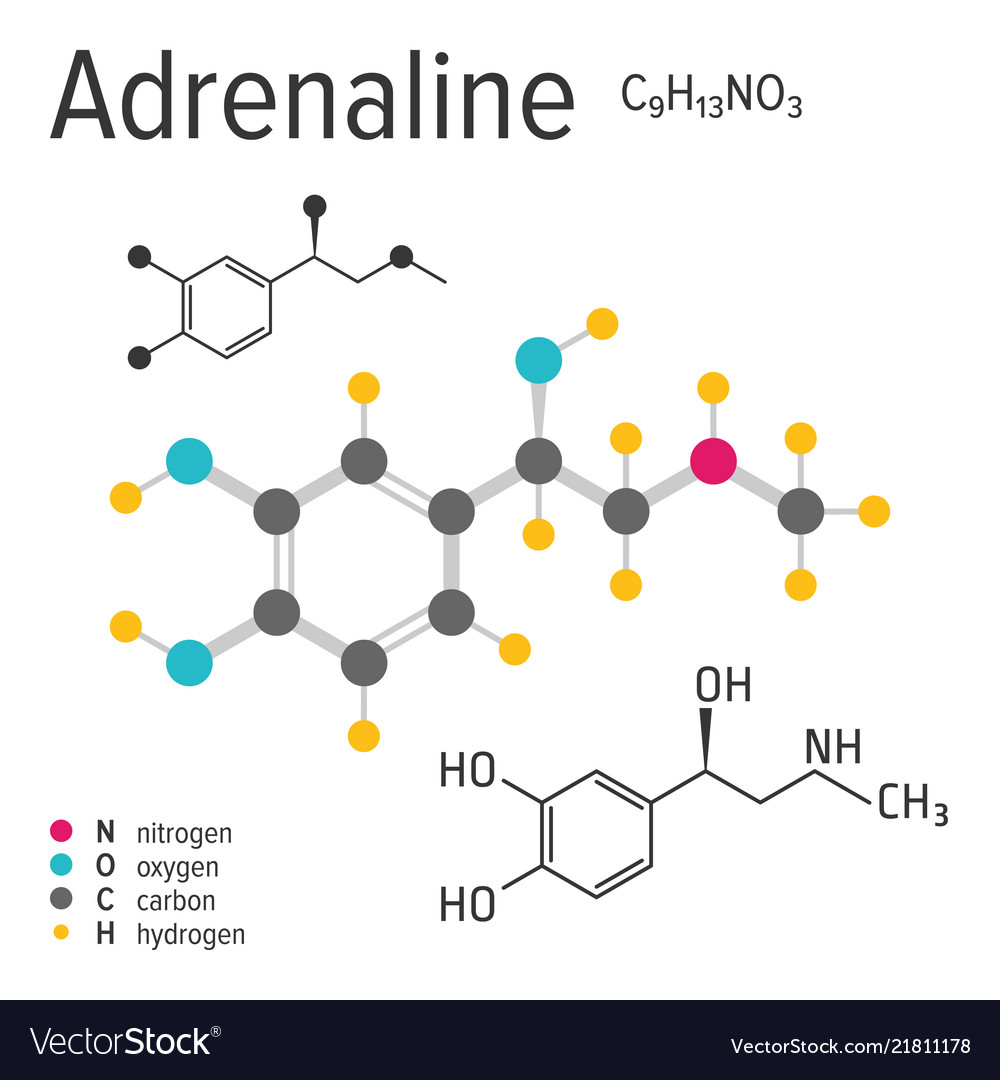
Chemical formula of the adrenaline molecule Vector Image
Adrenochrome is a chemical compound produced by the oxidation of adrenaline (epinephrine). It was the subject of limited research from the 1950s through to the 1970s as a potential cause of schizophrenia. While it has no current medical application, the related derivative compound, carbazochrome, is a hemostatic medication.

Adrenaline molecular chemical structural formula Vector Image
Background: Adrenaline is localized to specific regions of the central nervous system (CNS), but its role therein is unclear because of a lack of suitable pharmacologic agents. Ideally, a chemical is required that crosses the blood-brain barrier, potently inhibits the adrenaline-synthesizing enzyme PNMT, and does not affect other catecholamine processes. Currently available PNMT inhibitors do.

"Adrenaline, adrenalin Molecule" by erzebetth Redbubble
Key actions of adrenaline include increasing the heart rate, increasing blood pressure, expanding the air passages of the lungs, enlarging the pupil in the eye (see picture 1), decreasing the sensitivity to pain, improve vision, hearing and other senses, slowing digestion, redistributing blood to the muscles and altering the body's metabolism, s.

Adrenalin das ActionHormon wissenschaft.de
Adrenaline Noradrenaline Adrenergic receptors Agonists Antagonists Biological function Download chapter PDF 4.1 Introduction Adrenaline and noradrenaline are two important catecholamines, which are responsible for foremost activities in the maintenance of the "inner world" of the brain body.

Adrenaline (Epinephrine) Drug Detail Profile > PharmaCampus
Generic Name Epinephrine DrugBank Accession Number DB00668 Background. Epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, is a hormone and neurotransmitter and produced by the adrenal glands that can also be used as a drug due to its various important functions.Though it has long been used in the treatment of hypersensitivity reactions, epinephrine in the auto-injector form (EpiPen) has been available.

Adrenaline Chemical Structure. Vector Illustration Hand Drawn. Stock
Description Epinephrine appears as white to nearly-white microcrystalline powder or granules. Odorless. Melting point 211-212 °C. Aqueous solutions are slightly alkaline. Slightly bitter, numbing taste. CAMEO Chemicals (R)-adrenaline is the R-enantiomer of adrenaline.

"Adrenaline, adrenalin Molecule" by erzebetth Redbubble
ChemSpider Search and share chemistry For medical information relating to Covid-19, please consult the World Health Organisation or local healthcare provision. Simple Structure Advanced History Comment on this record 3D adrenaline Molecular Formula CHNO Average mass 183.204 Da Monoisotopic mass 183.089539 Da ChemSpider ID 815 More details: Names

Epinephrine Formula Chemical Molecule Adrenaline Molecular Structure
The chemical formula of epinephrine is C9H13NO3. Its structure is shown right. Epinephrine was first isolated and identified in 1897 by John Jacob Abel. Jokichi Takamine discovered the same hormone in 1901, without knowing about the previous discovery, and called it adrenaline. It was first artificially synthesized in 1904 by Friedrich Stolz.

Gaines, on Brains Superhero science tapping into our superstrength
organic chemistry - Why are there different chemical structures for epinephrine (adrenaline)? - Chemistry Stack Exchange Why are there different chemical structures for epinephrine (adrenaline)? Asked 9 years, 1 month ago Modified 4 years, 3 months ago Viewed 4k times 6 The Wikipedia structure is: Note the empty bond at far-right.

Adrenaline is a hormone chemical formula Vector Image
Adrenaline ( epinephrine) is a hormone your adrenal glands send through your bloodstream. When you're scared or stressed suddenly, adrenaline is quickly sent into your body. This is commonly known as an adrenaline rush because it happens so fast. You've probably heard of "fight or flight.". Adrenaline is what gets your body ready to.
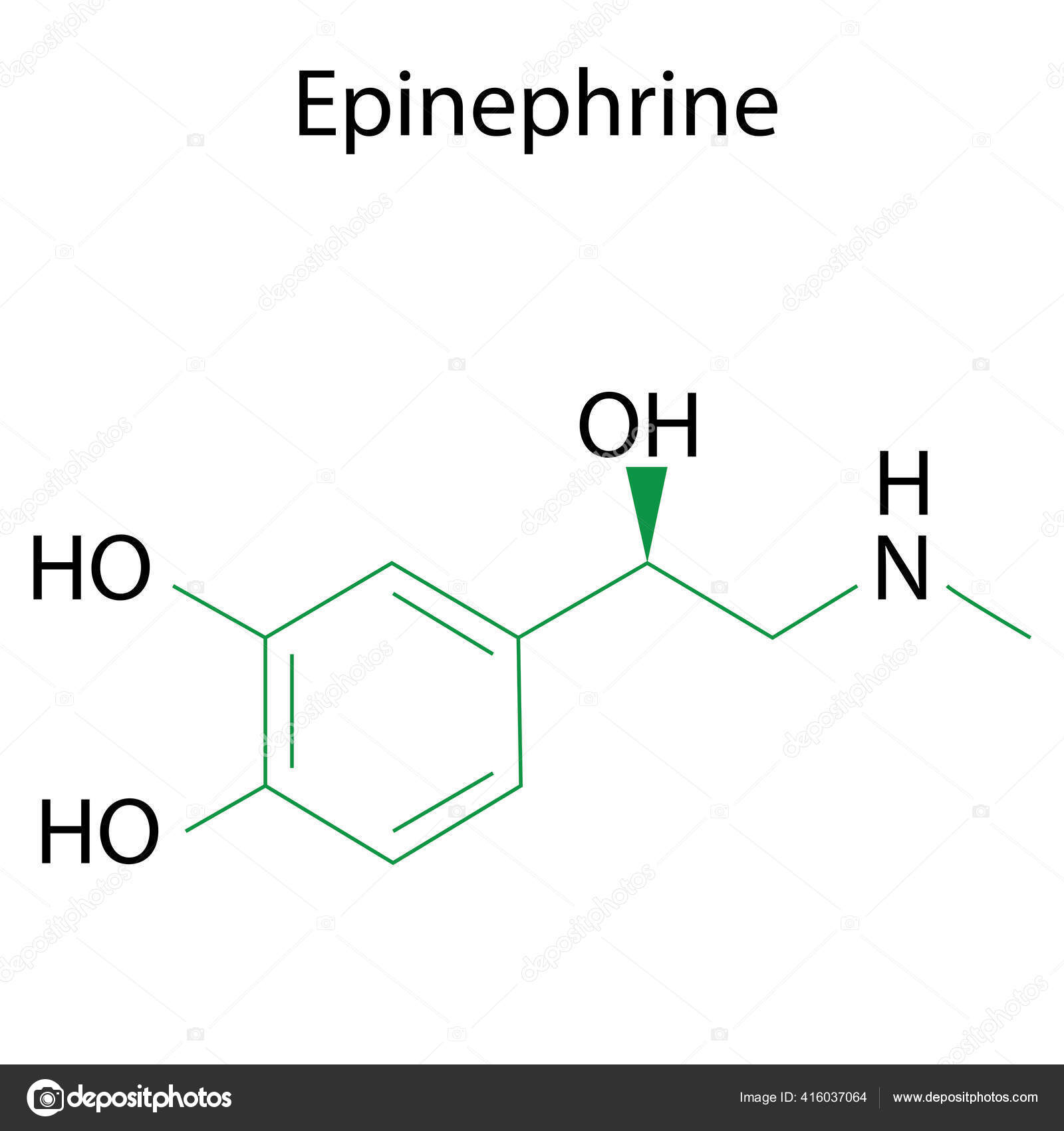
Epinephrine Formula Chemical Molecule Adrenaline Molecular Structure
Epinephrine (Adrenaline) Epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, is both a neurotransmitter and a hormone. It plays an important role in your body's "fight-or-flight" response. It's also used as a medication to treat many life-threatening conditions. What is epinephrine? Epinephrine, also called adrenaline, is both a hormone and a neurotransmitter.

Molecular structure of adrenaline, noradrenaline, isoprenaline
Structure Molecular Formula C9H13NO3 Synonyms DL-Adrenaline 329-65-7 dl-Epinephrine Racepinephrine Racepinefrine View More. Molecular Weight 183.20 g/mol Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2021.10.14) Dates Create: 2005-03-25 Modify: 2023-12-30 Description

Adrenaline Molecular Structure Epinephrine Skeletal Chemical Formula
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication [7] [8] which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). [7] [9] It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. [10] Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands and by a small number of neurons in the medulla oblongata. [11]

Adrenaline chemical formula. On white background , sponsored,
IUPAC Standard InChIKey: UCTWMZQNUQWSLP-VIFPVBQESA-N Copy CAS Registry Number: 51-43-4 Chemical structure: This structure is also available as a 2d Mol file or as a.
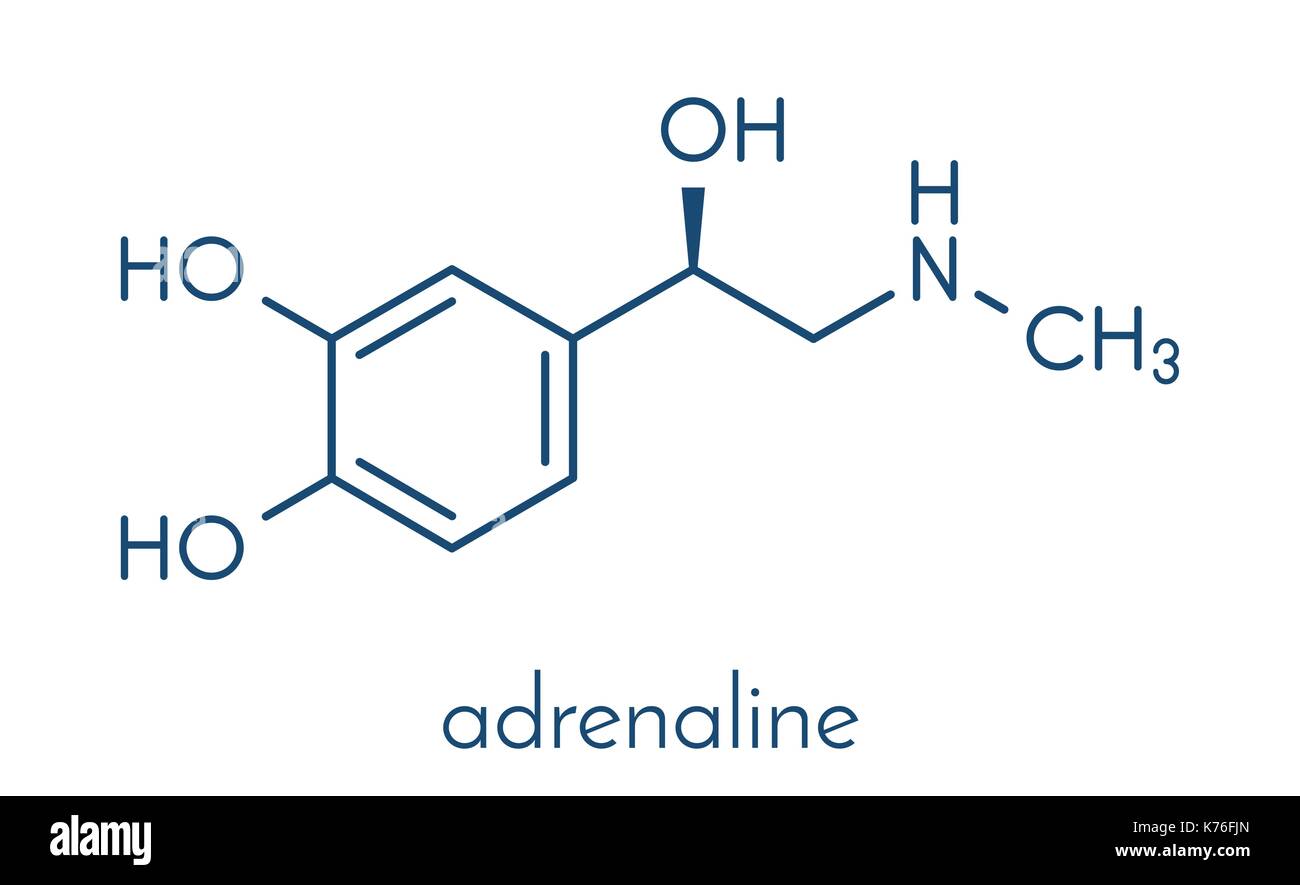
Adrenaline (adrenalin, epinephrine) neurotransmitter molecule. Used
The 2D chemical structure image of (S)-adrenaline is also called skeletal formula, which is the standard notation for organic molecules. The carbon atoms in the chemical structure of (S)-adrenaline are implied to be located at the corner(s) and hydrogen atoms attached to carbon atoms are not indicated - each carbon atom is considered to be associated with enough hydrogen atoms to provide the.